Absolutely! Here’s a 3000-word article about electric cars, structured with `
` and `
` tags instead of “ for a more organized, heading-based presentation.
The automotive landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the imperative to reduce carbon emissions and embrace sustainable transportation. At the heart of this shift lies the electric car, a vehicle powered by electricity rather than traditional fossil fuels. This article delves into the intricacies of electric cars, exploring their technology, benefits, challenges, and the future they herald.
What is an Electric Car?
An electric car, also known as an electric vehicle (EV), is a vehicle propelled by one or more electric motors, using electrical energy stored in rechargeable batteries or another energy storage device. Unlike internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles that rely on gasoline or diesel, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner air and a reduced carbon footprint.
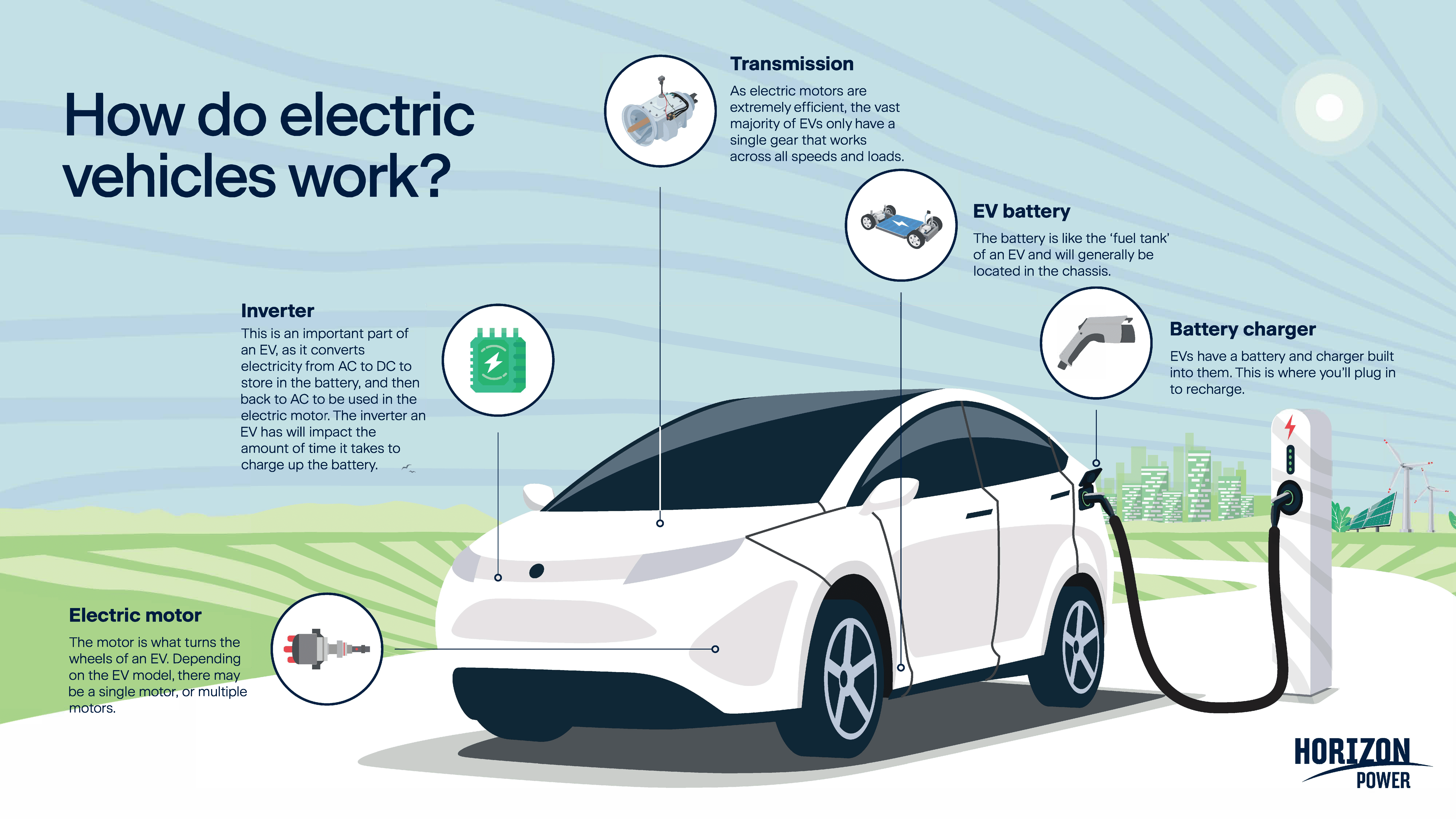
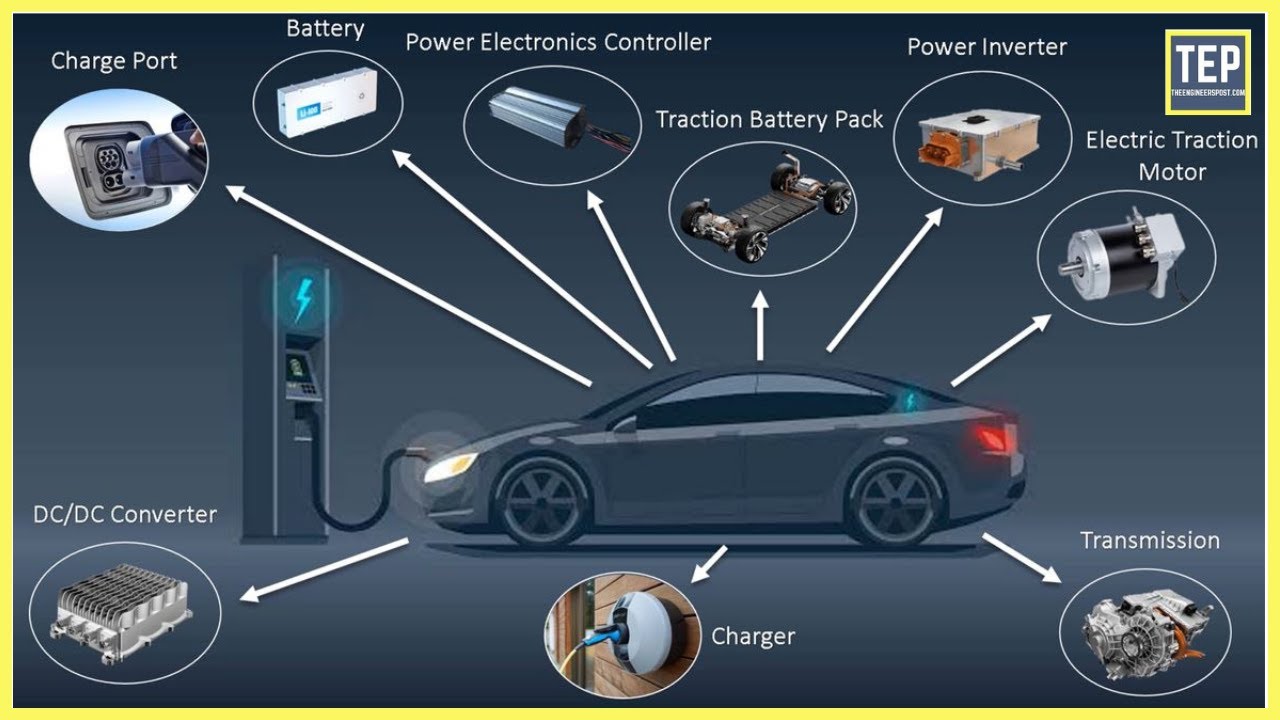
Key Components of an Electric Car
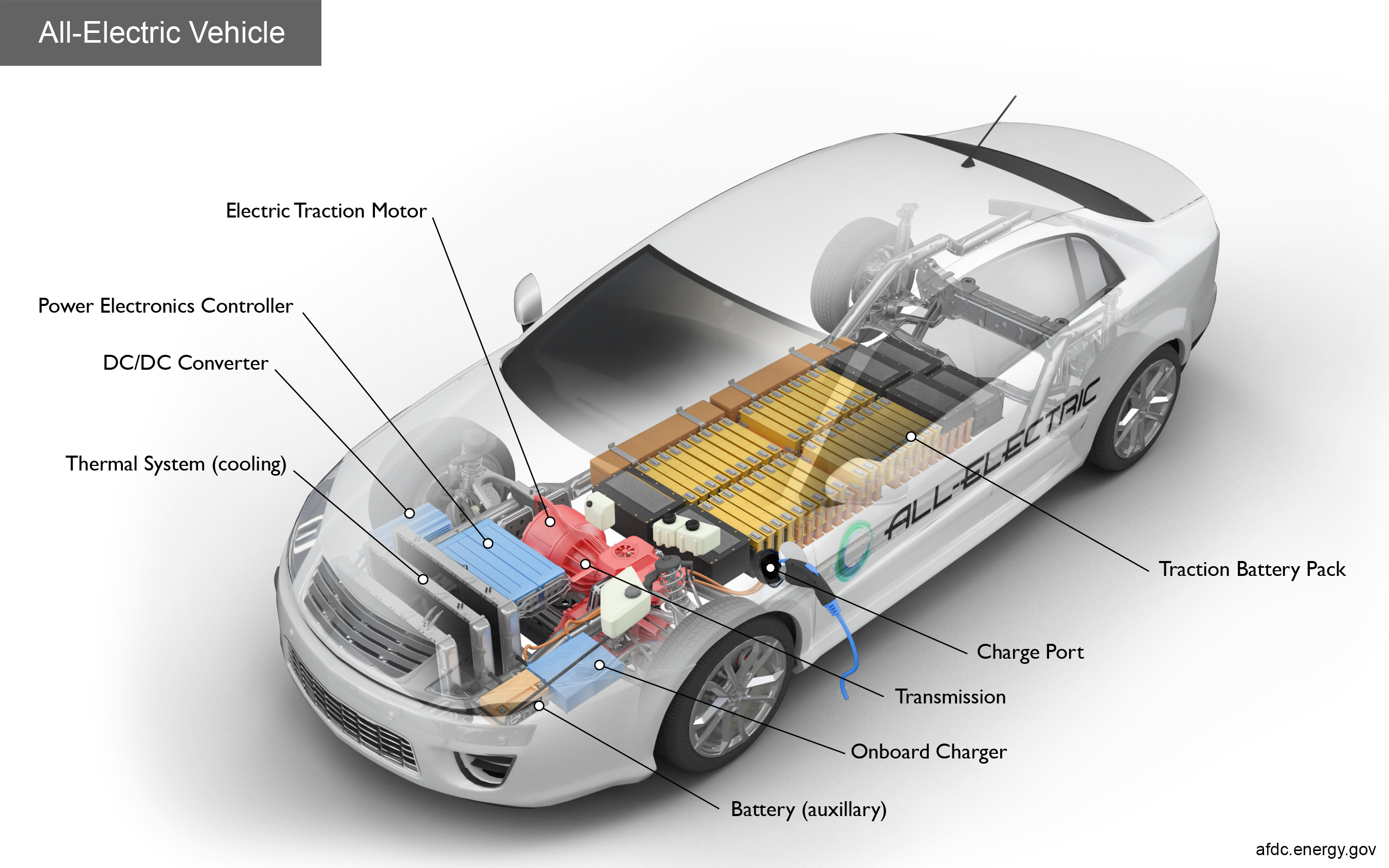
Battery: The battery is the heart of an EV, storing the electrical energy that powers the motor. Lithium-ion batteries are the most common type due to their high energy density and long lifespan.
Types of Electric Cars
The electric vehicle market encompasses various types of vehicles, each with its own characteristics and applications.
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
BEVs are fully electric vehicles that rely solely on batteries for power. They have no internal combustion engine and produce zero tailpipe emissions. Examples include the Tesla Model 3, Nissan Leaf, and Chevrolet Bolt EV.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)
PHEVs combine an electric motor with an internal combustion engine. They can be plugged in to recharge their batteries and can also operate on gasoline or diesel when the battery is depleted. Examples include the Toyota Prius Prime and the Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV.
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
HEVs use both an electric motor and an internal combustion engine, but they cannot be plugged in to recharge. The battery is recharged through regenerative braking and by the engine. Examples include the Toyota Prius and the Honda Insight. Although they use electric motors, they are not considered plug in electric vehicles.
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs)
FCEVs use hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, which powers the electric motor. They emit only water vapor and heat. Examples include the Toyota Mirai and the Hyundai Nexo.
Benefits of Electric Cars
The growing popularity of electric cars is driven by a range of compelling benefits.
Environmental Advantages
Zero Tailpipe Emissions: EVs produce no tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and contributing to cleaner urban environments.
Economic Advantages
Lower Running Costs: Electricity is often cheaper than gasoline or diesel, resulting in lower fuel costs.
Performance Advantages
Instant Torque: Electric motors provide instant torque, resulting in rapid acceleration.
Challenges of Electric Cars
Despite their numerous benefits, electric cars face several challenges that need to be addressed to accelerate their widespread adoption.
Range Anxiety
Limited Range: Some EVs have a limited driving range, which can cause anxiety for drivers who are concerned about running out of battery power.
High Initial Cost
Battery Cost: The battery is the most expensive component of an EV, contributing to the high initial purchase price.
Infrastructure Limitations
Grid Capacity: Increased EV adoption will require significant upgrades to the electricity grid to handle the increased demand.
The Future of Electric Cars
The future of electric cars looks promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and increasing government support.
Technological Advancements
Improved Battery Technology: Ongoing research is focused on developing batteries with higher energy density, faster charging times, and longer lifespans.
Government Policies and Incentives
Emission Regulations: Increasingly stringent emission regulations are driving the shift towards electric vehicles.
Market Growth
Increasing Consumer Demand: Growing consumer awareness of the environmental and economic benefits of EVs is driving demand.
In conclusion, electric cars represent a pivotal shift in the automotive industry, offering a cleaner, more sustainable, and increasingly viable alternative to traditional vehicles. While challenges remain, the ongoing advancements in technology, supportive government policies, and growing consumer demand suggest that the electric revolution is here to stay.



