Absolutely! Here’s a 3000-word article on Electric Vehicle ETFs, formatted with `
` and `
` tags in place of “ for a more structured, heading-based presentation.
—
The automotive industry is undergoing a monumental shift, driven by the relentless march of electric vehicles (EVs). This transformation is not just about cleaner transportation; it’s a profound economic and technological revolution that presents significant investment opportunities. For investors seeking exposure to this burgeoning sector, Electric Vehicle ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds) offer a compelling avenue.
The rise of EVs is fueled by a confluence of factors: growing environmental awareness, stringent government regulations, and rapid advancements in battery technology. As consumers increasingly embrace sustainable transportation, the demand for EVs is surging, creating a fertile ground for investment.
The Core Components of the EV Ecosystem
The EV ecosystem extends far beyond the assembly of electric cars. It encompasses a complex network of industries, each playing a crucial role in the sector’s growth.
Battery Technology and Manufacturing
The heart of an EV lies in its battery. Companies involved in battery production, raw material sourcing (lithium, cobalt, nickel), and battery management systems are pivotal to the industry’s expansion.
Electric Vehicle Manufacturers
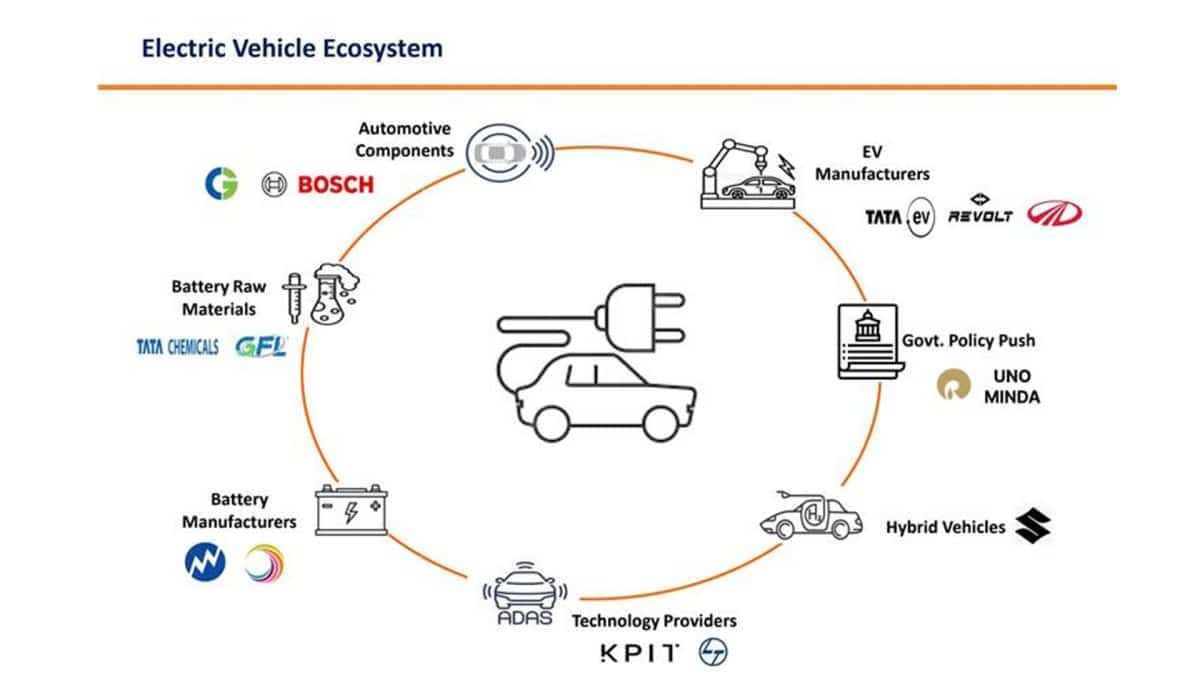
This segment includes established automakers transitioning to EVs and emerging pure-play EV companies. These companies are responsible for designing, manufacturing, and marketing electric vehicles.
Charging Infrastructure
The widespread adoption of EVs hinges on a robust charging infrastructure. Companies developing and deploying charging stations, as well as those involved in related technologies, are essential to the ecosystem.
Semiconductor and Software Providers
Modern EVs rely heavily on sophisticated semiconductors and software. Companies producing chips, sensors, and software for autonomous driving and vehicle management are critical players.
Raw Material Suppliers
The production of EV batteries requires substantial amounts of raw materials. Companies involved in mining and processing these materials are integral to the supply chain.
Why Invest in Electric Vehicle ETFs?

Investing in individual EV stocks can be risky due to the sector’s volatility and the competitive landscape. Electric Vehicle ETFs offer several advantages:
Diversification
ETFs provide exposure to a diversified portfolio of companies across the EV ecosystem, mitigating the risk associated with investing in a single stock.
Accessibility
ETFs are traded on major stock exchanges, making them easily accessible to retail and institutional investors.
Lower Expense Ratios
Compared to actively managed mutual funds, ETFs typically have lower expense ratios, reducing the cost of investment.
Transparency
ETFs disclose their holdings daily, providing investors with complete transparency into their investment portfolio.
Key Types of Electric Vehicle ETFs
Electric Vehicle ETFs can be broadly categorized based on their investment focus.
Pure-Play EV ETFs
These ETFs focus exclusively on companies directly involved in the design, manufacturing, and sale of electric vehicles.
Battery Technology ETFs
These ETFs concentrate on companies engaged in the development and production of EV batteries and related technologies.
Clean Energy and EV Infrastructure ETFs
These ETFs offer broader exposure to the clean energy sector, including EV charging infrastructure and renewable energy companies.
Global EV ETFs
These ETFs invest in a diversified portfolio of EV-related companies across global markets.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an EV ETF
Selecting the right EV ETF requires careful consideration of several factors.
Expense Ratio
The expense ratio represents the annual cost of owning the ETF. Lower expense ratios are generally preferable.
Tracking Index
Understanding the ETF’s tracking index is crucial, as it determines the fund’s investment strategy and holdings.
Holdings and Diversification
Evaluate the ETF’s holdings to ensure it aligns with your investment objectives. A well-diversified portfolio reduces risk.
Performance History
Review the ETF’s historical performance, but remember that past performance is not indicative of future results.
Liquidity
Ensure the ETF has sufficient trading volume to facilitate easy buying and selling.
Geographic Exposure
Determine the geographic focus of the ETF, as different regions may offer varying growth opportunities.
Risks and Challenges in the EV Sector
While the EV sector presents significant growth potential, it also faces several risks and challenges.
Technological Disruptions
Rapid technological advancements can render existing technologies obsolete, impacting the value of related investments.
Competition
The EV market is highly competitive, with numerous companies vying for market share.
Regulatory Changes
Government policies and regulations can significantly impact the EV sector, creating uncertainty.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The EV supply chain is complex and vulnerable to disruptions, such as raw material shortages or manufacturing bottlenecks.
Economic Fluctuations
Economic downturns can dampen consumer demand for EVs, affecting the performance of EV-related investments.
The Future of Electric Vehicle Investing
The EV revolution is still in its early stages, and the sector is poised for substantial growth in the coming decades. As technology continues to advance and infrastructure improves, the adoption of EVs is expected to accelerate.
Increased Adoption Rates
Governments worldwide are implementing policies to promote EV adoption, including subsidies, tax incentives, and emission regulations.
Advancements in Battery Technology
Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving battery energy density, reducing charging times, and lowering costs.
Expansion of Charging Infrastructure
Investments in charging infrastructure are essential to support the growing number of EVs on the road.
Integration of Autonomous Driving
The integration of autonomous driving technology into EVs is expected to enhance safety and convenience.
Sustainability and Circular Economy
The EV sector is increasingly focused on sustainability, with efforts to develop closed-loop battery recycling and reduce the environmental impact of manufacturing.
Examples of Prominent Electric Vehicle ETFs
Several ETFs offer exposure to the electric vehicle sector.
Global X Autonomous & Electric Vehicles ETF (DRIV)
This ETF invests in companies involved in autonomous vehicles and electric vehicles, including manufacturers, battery producers, and technology providers.
KraneShares Electric Vehicles & Future Mobility Index ETF (KARS)
This ETF tracks an index of companies engaged in the production of electric vehicles and related technologies.
iShares Self-Driving EV and Tech ETF (IDRV)
This ETF focuses on companies involved in autonomous vehicles, electric vehicles, and related technologies.
First Trust NASDAQ Global Auto Index Fund (CARZ)
This ETF provides exposure to global automakers, including those transitioning to electric vehicles.
VanEck Green Energy ETF (SMOG)
This ETF invests in companies involved in various green energy sectors, including electric vehicles and related technologies.
Conclusion
The electric vehicle revolution is transforming the automotive industry and creating significant investment opportunities. Electric Vehicle ETFs offer a diversified and accessible way to participate in this burgeoning sector. By carefully considering the factors discussed in this article, investors can make informed decisions and potentially capitalize on the long-term growth of the EV market. As the world transitions towards a more sustainable future, electric vehicles are poised to play a central role, making EV ETFs a compelling addition to a well-diversified investment portfolio. Investors should always conduct thorough research and consult with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions. The EV landscape is dynamic and requires continuous monitoring to stay ahead of the curve.


