Absolutely! Crafting a 3000-word article on the price of electric cars, with a focus on comprehensive information and using `
` and `
` tags for subheadings, is a substantial task. Here’s a structured outline and a sample of the article to give you a strong foundation:
1. Introduction:
2. Base Price and Vehicle Segments:
3. Factors Influencing EV Prices:
4. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO):
5. Charging Infrastructure and Costs:
6. Future Trends and Predictions:
7. Conclusion:

“`html
The Price of Electric Cars: A Comprehensive Guide
The electric vehicle (EV) revolution is in full swing, with more consumers than ever considering making the switch. However, a significant barrier to entry remains: the price. Understanding the factors that influence EV costs is crucial for making an informed decision. This article delves into the intricacies of EV pricing, from base costs to long-term ownership expenses.
Base Price and Vehicle Segments
EVs, like traditional vehicles, span a wide range of price points, categorized by vehicle segment. These segments help consumers understand the features and capabilities they can expect at different price levels.
Entry-Level EVs: Affordability and Limitations
Entry-level EVs are designed to be more accessible to budget-conscious buyers. These vehicles often prioritize affordability over extensive range or advanced features. Examples of these vehicles are the lower trim levels of the Nissan Leaf, or the Fiat 500e. These vehicles are designed for city driving, and shorter commutes. While they lower the barrier of entry, they tend to have smaller battery packs, and less advanced features.
Mid-Range EVs: Balancing Features and Cost

The mid-range segment offers a balance between affordability and features. These EVs typically provide a decent range, comfortable interiors, and a reasonable set of technology features. This is where most consumers will find the best value. This segment includes models such as the Tesla Model 3, the Hyundai Ioniq 5, and the Kia EV6. These cars are often pushing the boundaries of what is possible in their price ranges.
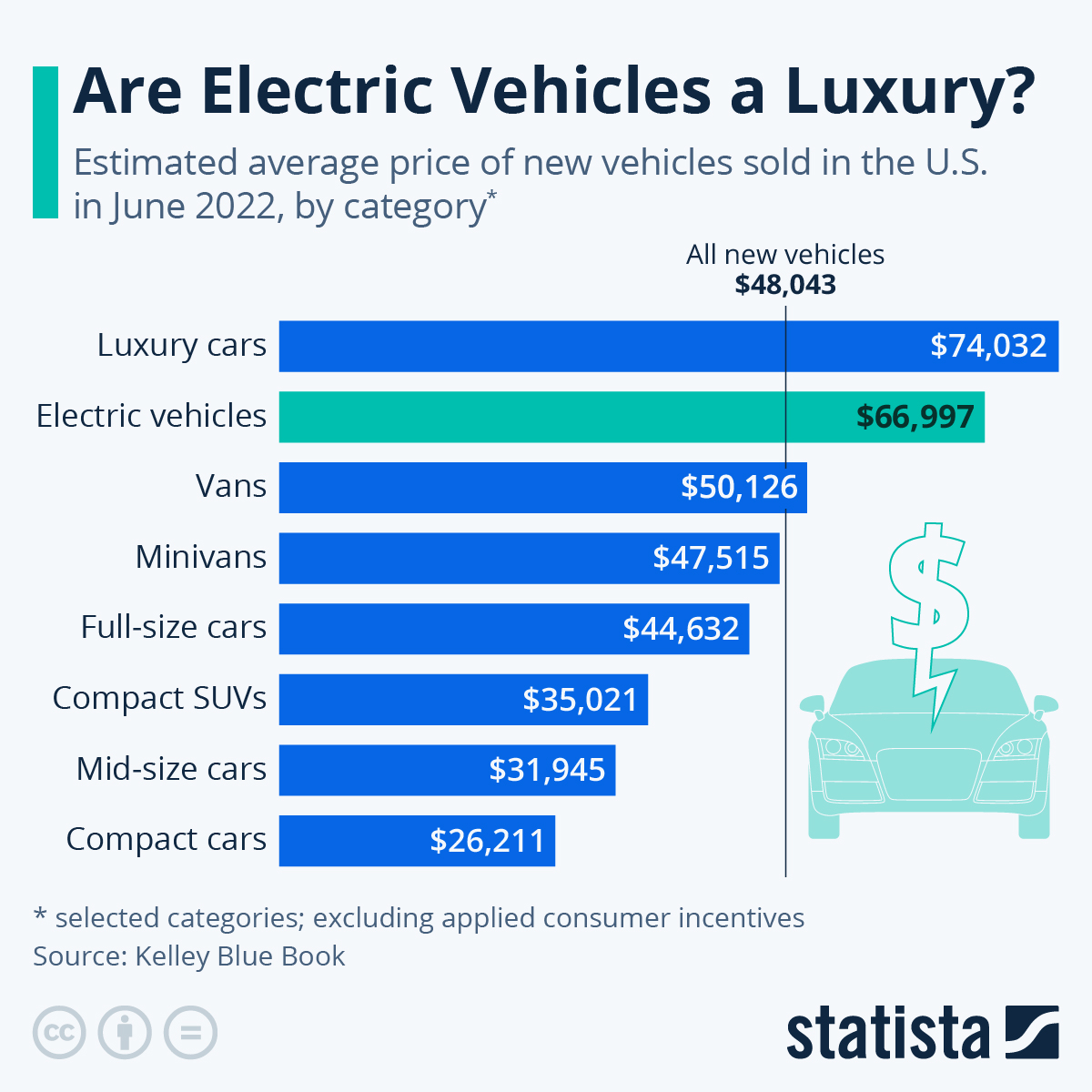
Premium EVs: Luxury, Performance, and High Price Tags
Premium EVs cater to buyers seeking luxury, performance, and cutting-edge technology. These vehicles often boast impressive acceleration, long ranges, and opulent interiors. Brands like Tesla (Model S, Model X), Mercedes-Benz (EQS), and Audi (e-tron GT) dominate this segment. These vehicles often include every available option, and push the limits of EV technology.
Factors Influencing EV Prices
Several factors contribute to the pricing of EVs, making it a complex equation for consumers to navigate.
Battery Technology and Capacity
The battery is the most expensive component of an EV, significantly impacting its overall price. Battery chemistry, capacity, and manufacturing costs all play a role.
The Impact of Battery Chemistry
Lithium-ion batteries are the most common type used in EVs. However, variations in chemistry, such as lithium iron phosphate (LFP), can affect cost and performance. LFP batteries, for example, are often more cost-effective but may offer lower energy density.
Range and Its Correlation with Battery Size
A longer driving range typically requires a larger battery pack, which increases the vehicle’s cost. Consumers must balance their range requirements with their budget.
Battery Production Costs
Raw material prices, manufacturing processes, and economies of scale all influence battery production costs. As technology advances and production scales up, battery prices are expected to decline.
Manufacturing and Production Costs
Beyond the battery, other manufacturing and production costs contribute to the final price.
Raw Material Sourcing and Prices
The sourcing of raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel can be volatile, affecting production costs. Supply chain disruptions can also exacerbate these issues.
Economies of Scale and Production Efficiency
As EV production increases, manufacturers can achieve economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs. Efficient manufacturing processes and automation also contribute to cost reduction.
Technology and Features
Advanced technology and features add to the allure of EVs but also increase their price.
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Features like adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and automatic emergency braking enhance safety but add to the vehicle’s cost.
Infotainment and Connectivity
Large touchscreens, premium audio systems, and advanced connectivity features contribute to the overall price.
Performance and Handling
High-performance EVs with powerful motors and advanced suspension systems command higher prices.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
While the initial purchase price is a significant consideration, understanding the total cost of ownership (TCO) is essential for evaluating the long-term affordability of an EV.
Fuel/Electricity Savings
EVs typically have lower running costs compared to gasoline-powered vehicles due to cheaper electricity costs and higher energy efficiency.
Maintenance and Repair Expenses
EVs generally require less maintenance than gasoline cars, as they have fewer moving parts. However, battery replacements and specialized repairs can be costly.
Resale Value and Depreciation
The resale value of EVs can vary depending on factors like battery health, technology advancements, and market demand. Depreciation rates are also a consideration.
Insurance Cost.
Due to the higher cost of EV’s, insurance can be more expensive than that of a similar gasoline powered car.
Charging Infrastructure and Costs
The availability and cost of charging infrastructure are critical factors for EV owners.
Home Charging Installation and Equipment
Installing a home charging station can add to the initial cost, but it offers convenience and lower charging rates.
Public Charging Network Fees
Public charging networks charge fees for using their stations, which can vary depending on the charging speed and provider.
Fast Charging vs. Slow Charging Costs
Fast charging is more expensive than slow charging, but it offers quicker charging times for long-distance travel.
Future Trends and Predictions
The EV market is constantly evolving, with several trends expected to shape future pricing.
Expected Advancements in Battery Technology
Advancements in battery technology, such as solid-state batteries, are expected to improve range, reduce costs, and enhance safety.
Projected Decrease in EV Prices
As production scales up and technology advances, EV prices are projected to decrease, making them more accessible to a broader audience.