“`html
Electric car Yearly Cost: A Comprehensive Breakdown
The allure of electric vehicles (EVs) is undeniable. With promises of cleaner emissions, smoother rides, and cutting-edge technology, they’re rapidly gaining traction. However, a crucial question remains for potential buyers: what is the true yearly cost of owning an electric car? This article delves deep into the various factors influencing EV ownership costs, providing a detailed breakdown to help you make an informed decision.
Initial Purchase Price and Depreciation
The upfront cost of an EV is often higher than a comparable gasoline-powered vehicle. However, this gap is narrowing as battery technology improves and production scales up. The initial price is just the beginning; depreciation is a significant factor to consider.
Factors Affecting Depreciation
Battery Technology: Rapid advancements in battery technology can make older models seem outdated, accelerating depreciation.
Government Incentives: Changes in tax credits and rebates can influence resale values.
Model Popularity: High-demand models tend to retain their value better.
Mileage and Condition: Like any car, an EV’s condition and mileage significantly impact its resale value.
Researching the expected depreciation of your chosen EV model is crucial. Websites and publications specializing in automotive reviews often provide depreciation forecasts.
Electricity Costs vs. Fuel Costs
One of the most significant cost differences between EVs and gasoline cars is the fuel source. EVs run on electricity, which is generally cheaper than gasoline. However, the exact cost depends on several factors.
Factors Affecting Electricity Costs
Electricity Rates: Electricity prices vary significantly by region and time of day.
Charging Efficiency: The efficiency of your EV and charging equipment affects the amount of electricity used.
Driving Habits: Aggressive driving and frequent use of climate control can increase energy consumption.
Charging Location: Home charging is typically cheaper than public charging.
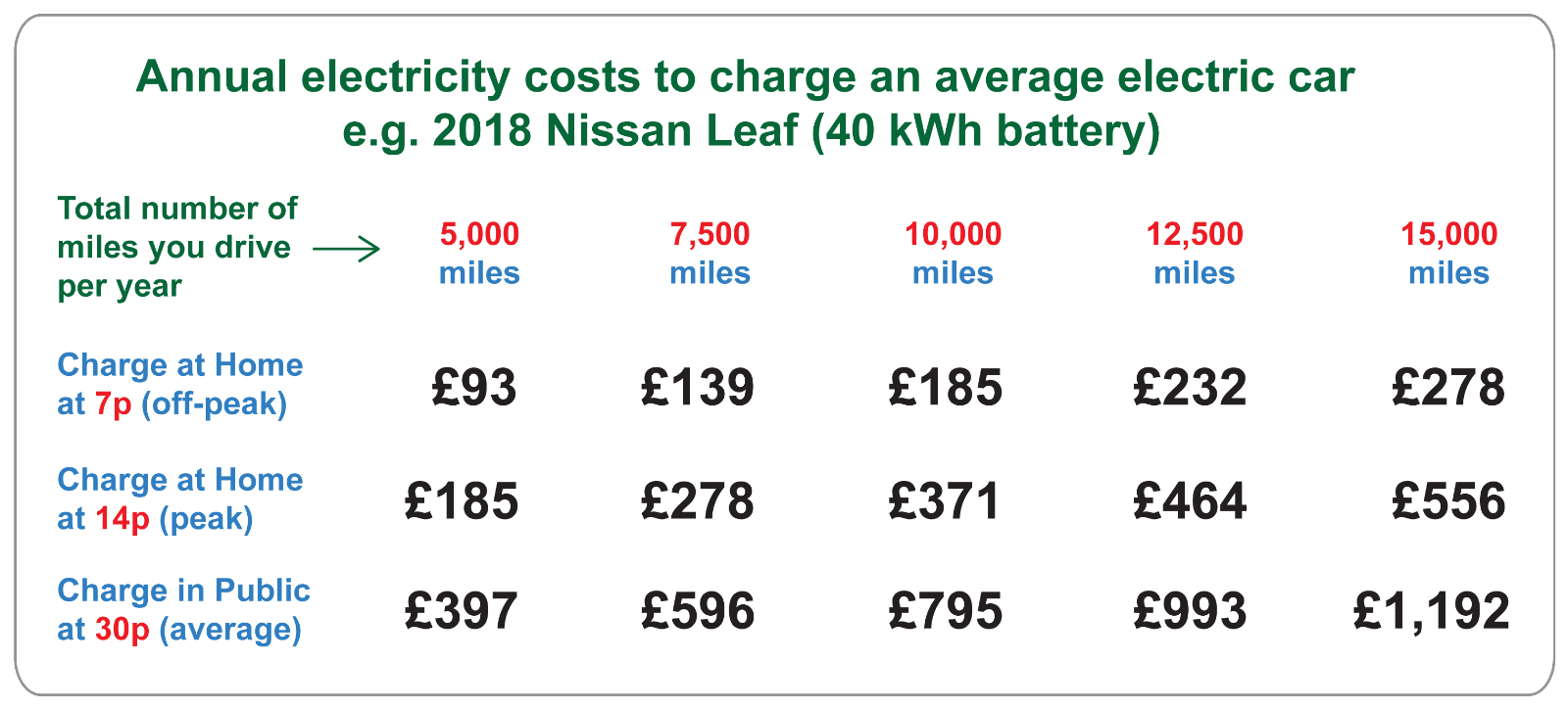
To calculate your yearly electricity cost, estimate your annual mileage and multiply it by the energy consumption of your EV (measured in kilowatt-hours per mile). Then, multiply that figure by your local electricity rate. Many EVs provide real-time energy consumption data, helping you track your usage.
Home Charging vs. Public Charging
Home charging is generally the most cost-effective option. Installing a Level 2 charger at home can significantly reduce charging times. Public charging, while convenient for long trips, is typically more expensive. Fast charging (DC fast charging) can be particularly pricey.
Maintenance and Repairs
EVs have fewer moving parts than gasoline cars, which translates to lower maintenance costs. There are no oil changes, spark plug replacements, or exhaust system repairs to worry about. However, EVs still require regular maintenance.
Common EV Maintenance Tasks
Tire Rotations and Replacements: EVs are often heavier than gasoline cars, leading to increased tire wear.
Brake Fluid Checks: While regenerative braking reduces wear on brake pads, brake fluid still needs to be checked and replaced.
Coolant Checks: EVs have cooling systems for the battery and motor, which require periodic checks.
Cabin Air Filter Replacement: Like any car, EVs have cabin air filters that need to be replaced.
Battery Health Checks: While EV batteries are designed to last, their health should be monitored.
While routine maintenance is generally less expensive, repairs can be costly, particularly for battery replacements. However, battery warranties often cover significant degradation within a specified timeframe. It’s crucial to understand your EV’s warranty coverage.
Insurance Costs
Insurance costs for EVs can vary significantly depending on several factors.
Factors Affecting EV Insurance Costs
Vehicle Value: EVs are often more expensive than gasoline cars, leading to higher premiums.
Repair Costs: The cost of repairing or replacing EV components can be higher.
Driving History: Your driving record plays a significant role in determining your insurance rate.
Coverage Options: Comprehensive coverage, including battery replacement, will increase premiums.
Location: Insurance rates vary by region.
It’s advisable to obtain multiple insurance quotes before purchasing an EV. Some insurers offer discounts for EVs, so it’s worth inquiring about available incentives.
Taxes and Incentives
Government incentives can significantly reduce the overall cost of EV ownership. These incentives vary by region and can include tax credits, rebates, and exemptions from vehicle registration fees.
Common EV Incentives
Federal Tax Credits: Many countries offer federal tax credits for EV purchases.
State and Local Rebates: Some states and local governments offer additional rebates.
HOV Lane Access: EVs may be eligible for access to high-occupancy vehicle lanes.
Reduced Registration Fees: Some regions offer reduced vehicle registration fees for EVs.
Researching available incentives in your area is crucial to accurately calculating the overall cost of EV ownership. Changes to these programs can dramatically alter the financial landscape. Also, be aware of when these incentives expire.
Depreciation and Resale Value Over Time
As mentioned earlier, depreciation is a significant factor in the long-term cost of EV ownership. Predicting future resale values can be challenging, but several trends are emerging.
Factors Influencing Future Resale Values
Battery Technology Advancements: Improvements in battery technology will likely continue to impact resale values.
Charging Infrastructure: The expansion of public charging infrastructure will likely increase demand for EVs.
Government Policies: Future government policies regarding emissions and incentives will play a role.
Consumer Demand: Growing consumer awareness and demand for EVs will influence resale values.
While predicting the future is impossible, staying informed about industry trends and technological advancements can help you make informed decisions about your EV purchase.
Calculating Your Total Yearly EV Cost
To calculate your total yearly EV cost, consider the following factors:
Yearly Cost Components
Depreciation: Estimate the annual depreciation of your chosen EV model.
Electricity Costs: Calculate your annual electricity costs based on your driving habits and local rates.
Maintenance and Repairs: Factor in the cost of routine maintenance and potential repairs.
Insurance Costs: Obtain insurance quotes to estimate your annual premiums.
Taxes and Fees: Consider any applicable taxes and fees, minus available incentives.
By adding these costs together, you can arrive at a comprehensive estimate of your yearly EV ownership expenses. Remember to adjust these calculations based on your specific circumstances and driving habits.
Long-Term Savings and Benefits
While the initial cost of an EV may be higher, long-term savings can be significant. Lower fuel and maintenance costs can offset the initial investment over time. Additionally, EVs offer several intangible benefits.
Benefits of EV Ownership
Reduced Emissions: EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner air.
Smoother Ride: EVs offer a quiet and smooth driving experience.
Technological Advancements: EVs often feature cutting-edge technology and connectivity.
Reduced Noise Pollution: EVs are significantly quieter than gasoline cars.
These benefits, combined with potential long-term savings, make EVs an increasingly attractive option for many consumers.
Conclusion
The yearly cost of owning an electric car is a complex equation with many variables. However, by carefully considering the factors outlined in this article, you can make an informed decision about whether an EV is right for you. While the initial purchase price may be higher, long-term savings on fuel and maintenance, combined with government incentives and environmental benefits, can make EVs a cost-effective and sustainable transportation choice. Thorough research, careful planning, and a realistic assessment of your driving needs are essential to maximizing the benefits of EV ownership.
“`



