Absolutely! Here’s a comprehensive article about electric car charging times, structured with `
` and `
` tags instead of “ tags, and aiming for a 3000-word length.
The electric vehicle (EV) revolution is upon us, bringing with it a wave of innovation and a shift towards sustainable transportation. However, one of the most frequently asked questions by potential EV owners revolves around charging times. How long does it really take to charge an electric car? The answer, as you’ll discover, is multifaceted.
Understanding the Basics of EV Charging
Before diving into specific charging times, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental concepts that influence how quickly an EV battery replenishes its energy.
Battery Capacity (kWh)
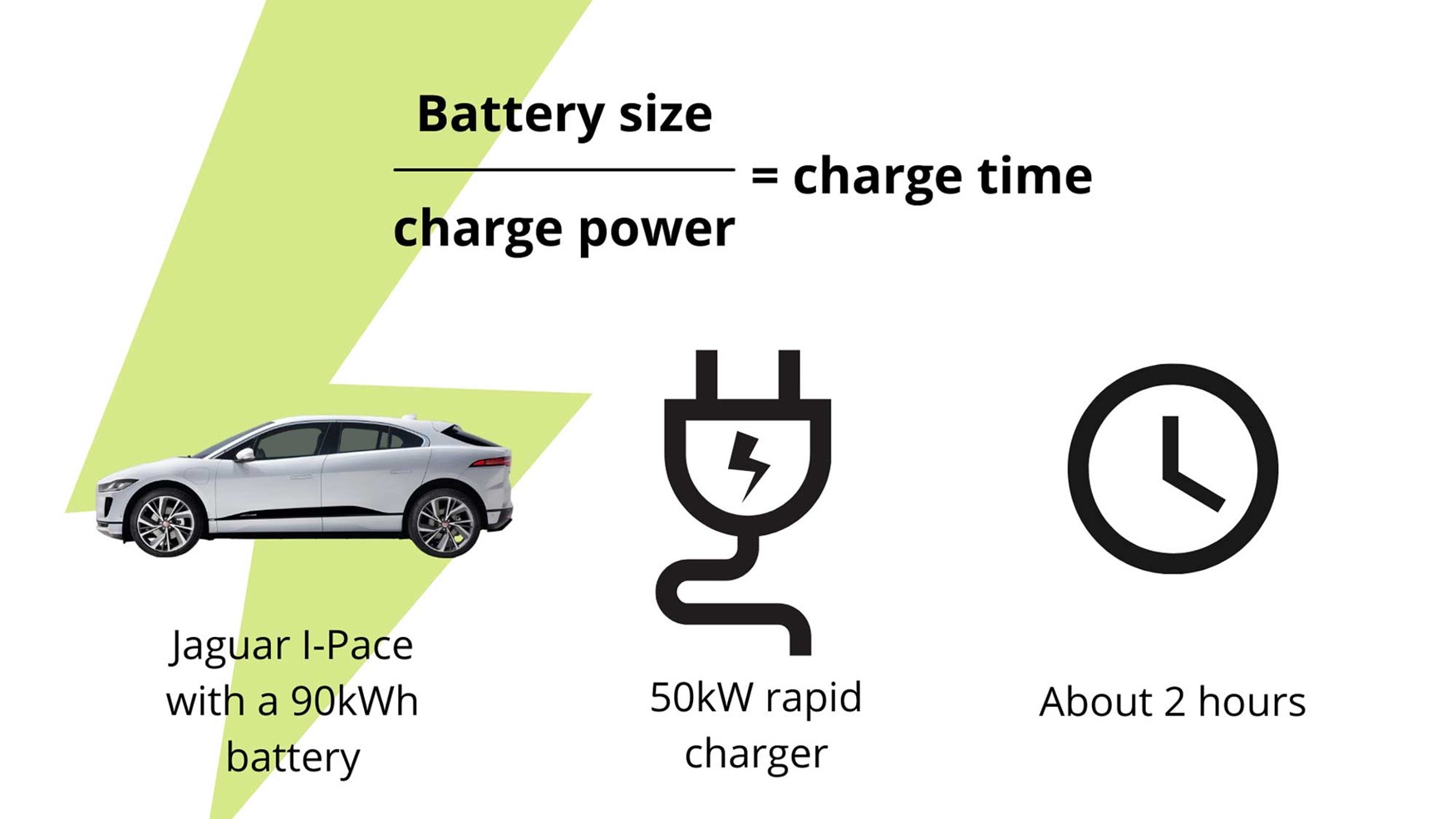
The battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), represents the amount of energy a battery can store. A higher kWh rating generally translates to a longer driving range. However, it also means potentially longer charging times.
Charging Power (kW)
Charging power, measured in kilowatts (kW), indicates the rate at which electricity flows into the battery. A higher kW rating results in faster charging.
Charging Standards and Connectors
Different charging standards and connectors exist, influencing the maximum charging power an EV can accept. Common standards include:
AC Charging (Level 1 and Level 2): Primarily used for home charging or public charging stations.
On-Board Charger
.png?width=1280&name=Understanding%20electricity%20(2).png)
Every EV has an on-board charger that converts AC power from the charging source to DC power for the battery. This charger has a maximum power rating, which limits the charging speed even if the charging station provides higher power.
State of Charge (SoC)
The SoC refers to the current level of energy in the battery, expressed as a percentage. Charging times vary depending on the initial SoC. Charging from 20% to 80% is generally faster than charging from 80% to 100%.
Temperature
Battery performance and charging speed are influenced by temperature. Extreme temperatures can slow down charging or even damage the battery.
Level 1 Charging: The Slowest Option
Level 1 charging uses a standard 120-volt household outlet. It’s the most basic charging method, often used as a backup option.
Typical Charging Times
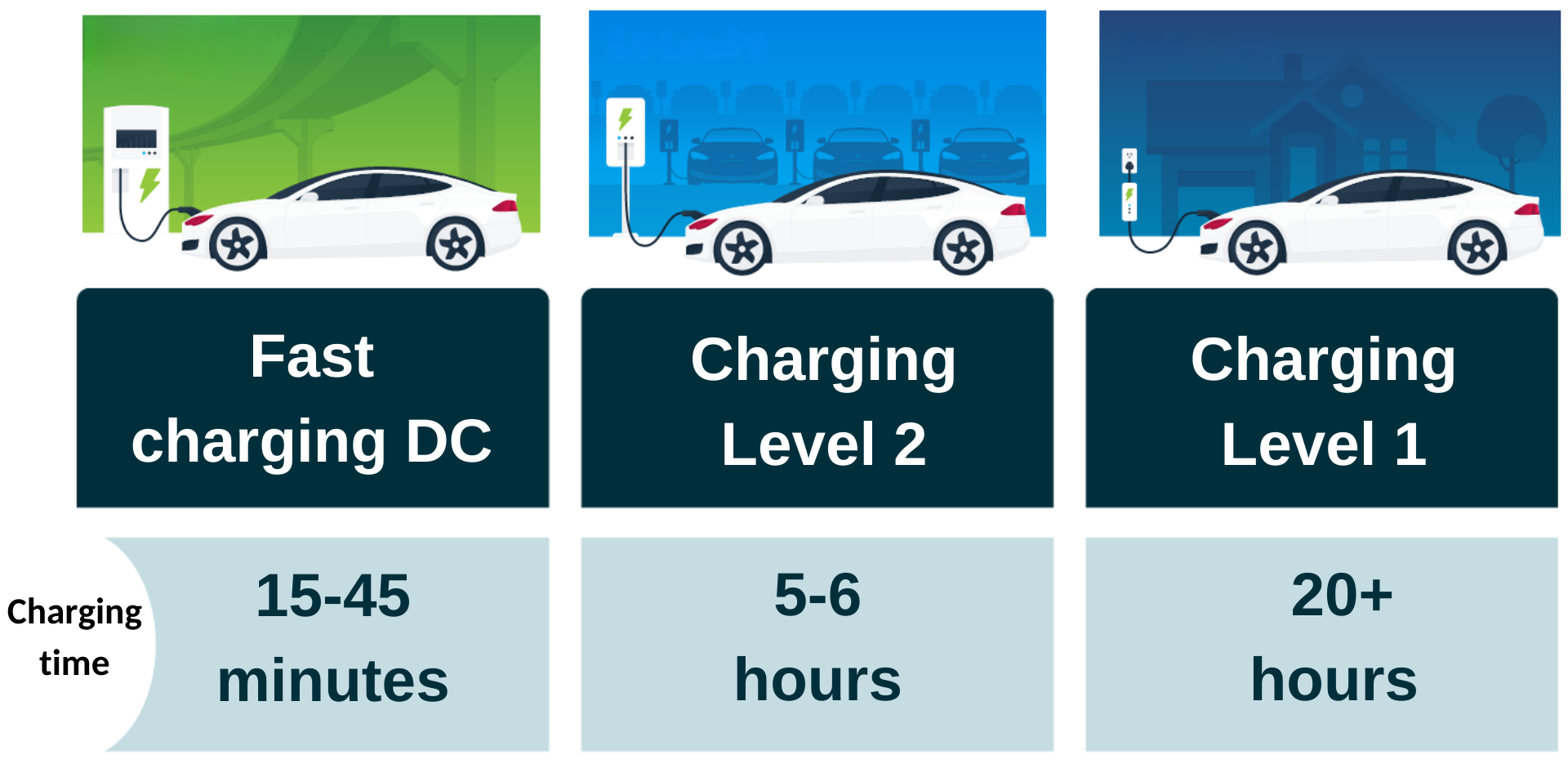
Level 1 charging provides approximately 3-5 miles of range per hour. For a typical EV with a 60 kWh battery, a full charge can take 24-48 hours. This method is best suited for overnight charging or for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) with smaller batteries.
Advantages
Requires no additional equipment.
Disadvantages
Extremely slow charging speeds.
Level 2 Charging: The Most Common Home Charging Solution
Level 2 charging utilizes a 240-volt circuit, similar to those used for electric dryers or ovens. It requires a dedicated charging station and installation by an electrician.
Typical Charging Times
Level 2 charging provides 10-60 miles of range per hour, depending on the charging station’s power rating and the EV’s on-board charger. A 60 kWh battery can be charged in 4-10 hours.
Factors Affecting Level 2 Charging Times
Charging Station Power: Level 2 chargers typically offer power ratings from 3.3 kW to 19.2 kW.
Advantages
Significantly faster than Level 1 charging.
Disadvantages
Requires installation of a dedicated charging station.
DC Fast Charging: Rapid Charging for Long Trips
DC fast charging, also known as Level 3 charging, uses high-power direct current (DC) to charge EVs at rapid speeds. These chargers are typically found at public charging stations along highways and in urban areas.
Typical Charging Times
DC fast charging can add 100-200 miles of range in 20-30 minutes, depending on the charger’s power rating and the EV’s charging capabilities. Some newer DC fast chargers can deliver power up to 350 kW, enabling even faster charging.
Factors Affecting DC Fast Charging Times
Charger Power Rating: DC fast chargers offer power ratings from 50 kW to 350 kW and beyond.
Advantages
Extremely fast charging speeds.
Disadvantages
Higher cost per kWh compared to Level 2 charging.
Real-World Charging Examples
To illustrate the differences in charging times, let’s look at some real-world examples:
Example 1: Nissan Leaf (40 kWh Battery)
Level 1: Approximately 16-20 hours for a full charge.
Example 2: Tesla Model 3 (Long Range, approximately 75 kWh battery)
Level 1: Approximately 30-40 hours for a full charge.
Example 3: Ford Mustang Mach-E (Extended Range, approximately 98 kWh battery)
Level 1: More than 40 hours for a full charge.
Tips for Optimizing EV Charging Times
Install a Level 2 charger at home: For convenient and faster daily charging.
The Future of EV Charging
The field of EV charging is constantly evolving, with ongoing advancements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and charging standards.
Ultra-Fast Charging
The development of ultra-fast charging technology, with power ratings exceeding 350 kW, is paving the way for even quicker charging times.
Wireless Charging
Wireless charging, which eliminates the need for cables, is another promising technology that could simplify the charging process.
Smart Charging
Smart charging systems use data and algorithms to optimize charging schedules and reduce electricity costs.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G)
V2G technology enables EVs to send energy back to the grid, providing grid stabilization and backup power.
Conclusion
Understanding EV charging times is crucial for making informed decisions about EV ownership. While charging times vary depending on several factors, including battery capacity, charging power, and charging standards, the advancements in charging technology are making EV ownership more convenient than ever before. As charging infrastructure continues to expand and charging speeds increase, the transition to electric mobility will become smoother and more accessible for everyone.



